Searching for Yandex Cloud events in Yandex Query
Audit Trails support is integrated in Yandex Query. You can analyze events of Yandex Cloud resources by executing analytical and streaming YQL queries.
You can execute analytical queries for logs stored in a bucket and streaming queries for logs stored in a Yandex Data Streams data stream.
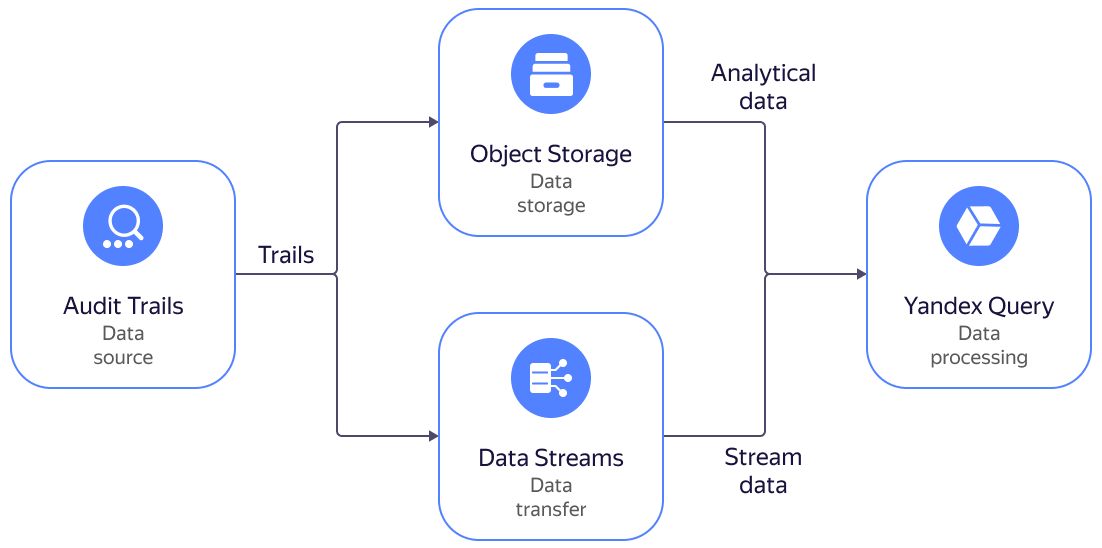
To connect a bucket with audit logs to Yandex Query and execute YQL queries:
- Prepare the environment.
- Create a connection between a trail and YQ.
- Execute a query to logs in Object Storage.
If you no longer need the resources you created, delete them.
Getting started
Sign up for Yandex Cloud and create a billing account:
- Go to the management console
- On the Yandex Cloud Billing
ACTIVEorTRIAL_ACTIVEstatus. If you do not have a billing account, create one.
If you have an active billing account, you can go to the cloud page
Learn more about clouds and folders.
If you do not have the Yandex Cloud command line interface yet, install and initialize it.
Required paid resources
The cost of infrastructure support includes a fee for a bucket (see Pricing for Object Storage).
Prepare the environment
Create a bucket for audit logs
- In the management console
example-folder. - Select Object Storage.
- Click Create bucket.
- On the bucket creation page:
- Enter a name for the bucket according to the naming requirements.
- In the Object read access, Object listing access, and Read access to settings fields, select
Restricted. - For the other parameters, leave the default settings.
- Click Create bucket.
Create service accounts
Create a service account named trail-sa:
- In the management console
example-folder. - At the top of the screen, go to the Service accounts tab.
- Click Create service account.
- Enter the Name:
trail-sa. - Click Create.
Use the same method to create a service account named bucket-yq-sa.
Assign rights to service accounts
Assign the audit-trails.viewer and storage.uploader roles to the trail-sa service account:
-
The
audit-trails.viewerrole to the organization:yc organization-manager organization add-access-binding \ --role audit-trails.viewer \ --id <organization_ID> \ --service-account-id <service_account_ID>Where
--service-account-idis the ID of thetrail-saservice account.Result:
done (1s)For more information about the
yc resource-manager organization add-access-bindingcommand, see the CLI reference. -
The
storage.uploaderrole toexample-folder:yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding example-folder \ --role storage.uploader \ --subject serviceAccount:<service_account_ID>Where
--subjectis the ID of thetrail-saservice account.Result:
done (1s)For more information about the
yc resource-manager folder add-access-bindingcommand, see the CLI reference.
Assign the bucket-yq-sa service account the storage.viewer role to example-folder:
yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding example-folder \
--role storage.viewer \
--subject serviceAccount:<service_account_ID>
Where --subject is the ID of the bucket-yq-sa service account.
Result:
done (1s)
For more information about the yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding command, see the CLI reference.
Create a trail
-
In the management console
example-folder. -
Select Audit Trails.
-
Click Create trail.
-
In the Name field, specify
logsyq. -
Under Destination, set up the destination object:
- Destination:
Object Storage. - Bucket: Select the previously created bucket.
- Destination:
-
Under Service account, select
trail-sa. -
Under Collecting events from the configuration level (Control plane), set up the collection of management event audit logs:
- Collecting events: Select
Enabled. - Resource: Select
Organization. - Organization: Automatically populated field containing the name of the current organization.
- Cloud: Keep the default value,
All.
- Collecting events: Select
-
Under Collecting events from the service level (Data plane), select
Disabledin the Collecting events field. -
Click Create.
Create a connection between a trail and YQ
A connection must be created only the first time a trail is connected to YQ.
- In the management console
example-folder. - Select Audit Trails.
- Select the
logsyqtrail. - Click Process in YQ.
- Create a connection.
- Select the Service account:
bucket-yq-sa. - For the other parameters, leave the default settings.
- Select the Service account:
- Click Create.
- In the window with data binding options, click Create.
You will go to the page for creating a query to trail logs.
Execute a query to logs in Object Storage
Open the page to create an analytical query to Audit Trails logs:
- In the management console
- In the list of services, select Audit Trails.
- Select the trail for which a connection to YQ is configured.
- Click Process in YQ to go to the analytical query execution page.
Execute event queries to bind audit-trails-logsyq-object_storage:
-
Deleting a folder:
-
From the list, select query 1. Find out who deleted a folder.
-
Edit the query by specifying the folder ID:
SELECT * FROM bindings.`audit-trails-logsyq-object_storage` WHERE JSON_VALUE(data, "$.event_type") = 'yandex.cloud.audit.resourcemanager.DeleteFolder' and JSON_VALUE(data, "$.details.folder_name") = '<folder_ID>' LIMIT 100; -
Click Execute.
-
-
Enabling access via the serial console:
-
From the list, select query 6. Changing a VM: Adding access to the serial console.
-
Edit the query by specifying the number of displayed records:
SELECT * FROM bindings.`<audit-trails-logsyq-object_storage>` WHERE JSON_VALUE(data, "$.event_type") = 'yandex.cloud.audit.compute.UpdateInstance' and JSON_VALUE(data, "$.details.metadata_serial_port_enable") = '1' LIMIT <number_of_records>; -
Click Execute.
-
-
Changing access rights to an Object Storage bucket:
-
From the list, select query 11. Suspicious activities with the Audit Trails log repository (Object Storage Bucket).
-
Edit the query by specifying the number of displayed records:
SELECT * FROM bindings.`audit-trails-logsyq-object_storage` WHERE (JSON_VALUE(data, "$.event_type") = 'yandex.cloud.audit.storage.BucketAclUpdate' or JSON_VALUE(data, "$.event_type") = 'yandex.cloud.audit.storage.BucketPolicyUpdate') LIMIT <number_of_records>; -
Click Execute.
-
-
Assigning administrator rights:
-
From the list, select query 20. Assigning admin rights (for resources: folder, cloud).
-
Edit the query by specifying the number of displayed records:
SELECT * FROM bindings.`audit-trails-logsyq-object_storage` WHERE JSON_VALUE(data, "$.details.access_binding_deltas.access_binding.role_id") = 'admin' LIMIT <number_of_records>; -
Click Execute.
-
How to delete the resources you created
If you created a separate bucket to follow these instructions, you can delete it to stop paying for bucket use.